- 8086 Microprocessor Architecture Pdf
- Block Diagram Of 8086 Microprocessor
- Difference Between 8086 And 80286 Microprocessor Pdf File

Assignment on summary of 80286, 80386, 80486 and pentium microprocessor submitted by: er. AMIT MAHAJAN 80286 microprocessor: Basically this microprocessor is an advanced version of 8086. So before starting with 80286 we must know something about 8086. Differences between 8086 and 8088 Microprocessor 8086. Download emu8086 with license key. Intel 80286: The Intel 80286 (often called simply the 286) was a 16-bit microprocessor chip introduced in 1982. It quickly became popular in PCs (personal computers) and could be found in many machines into the 1990s. The 80286 introduced a new generation of microprocessors with memory management. It also offered more than twice as much. Differences between 8085 and 8086 microprocessor; 8086 program to find GCD of two numbers and print the GCD; 8086 program to sort an integer array in ascending order; 8086 program to divide a 16 bit number by an 8 bit number; Flag register of 8086 microprocessor; 8086 program to subtract two 16-bit numbers with or without borrow. There are some of the difference mentioned below: 1.Size:- 8085 is 8 bit microprocessor whereas 8086 is 16 bit microprocessor. 2.Address Bus:- 8085 has 16 bit address bus and 8086 has 20 bit addres bus. 3.Memory:- 8085 can access upto 2^16 = 64 Kb. 80286 Microprocessor is a 16-bit microprocessor that has the ability to execute 16-bit instruction at a time. It has non-multiplexed data and address bus. The size of data bus is 16-bit whereas the size of address bus is 24-bit. It was invented in February 1982 by Intel. 80286 microprocessor was basically an advancement of 8086 microprocessor.Further in 1985, Intel produced upgraded version of.
80286 Microprocessor is a 16-bit microprocessor that has the ability to execute 16-bit instruction at a time. It has non-multiplexed data and address bus. The size of data bus is 16-bit whereas the size of address bus is 24-bit.
It was invented in February 1982 by Intel. 80286 microprocessor was basically an advancement of 8086 microprocessor. Further in 1985, Intel produced upgraded version of 80286 which was a 32-bit microprocessor.
Now the question arises what are the factors that make 80286 more advantageous than 8086 microprocessor?
- It has non-multiplexed address and data bus that reduces operational speed.
- The addressable memory in case of 80286 is 16 MB.
- It offers an additional adder for address calculation.
- 80286 has faster multipliers that lead to quick operation.
- The performance per clock cycle of 80286 is almost twice when compared with 8086 or 8088.
Operating modes of 80286 microprocessor
80286 operates in two modes:
In real address mode, this microprocessor acts as a version of 8086 which is quite faster. Also without any special modification, the instruction programmed for 8086 can be executed in 80286. It offers memory addressability of 1 MB of physical memory.
The protected virtual-address mode of 80286 supports multitasking because multiple programs can be executed using virtual memory. This mode of 80286 offers memory addressability of 16 MB of physical memory along with 1 GB of virtual memory.
As using virtual memory, space for other programs can be saved. Sometimes bulky programs also do exist that cannot be stored in physical memory, so virtual memory is utilized in order to execute large programs.
This mode is used in 80286, so that in case of memory failure in real address mode, it can stay in protected manner.
What is virtual memory?
Virtual memory is that part of hard disk which can be utilized for storing large instructions inside the system. This extra memory can be addressed by the computer other than the physical memory.
When there exists an instruction that is to be loaded in the memory but whose size is greater than the provided physical memory. Then some part of hard disk is used in order to store that instruction, which is known as virtual memory.
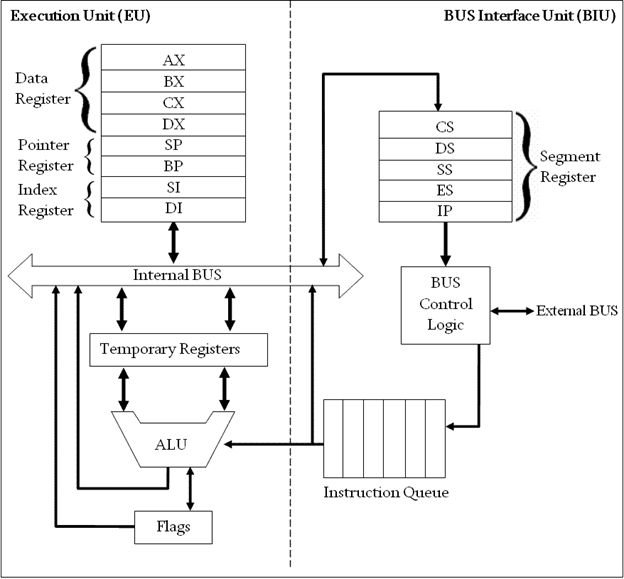
Architecture of 80286 Microprocessor
The figure below shows the architectural representation of 80286 microprocessor:
As we have already mentioned earlier that it is a 16-bit microprocessor thus holds a 16-bit data bus and 24-bit address bus. Also, unlike the 8086 microprocessor, it offers non-multiplexed address and data bus, which increases the operating speed of the system.
80286 is composed of nearly around 125K transistors and the pin configuration has a total of 68 pins.
The CPU, central processing unit of 80286 microprocessor, consists of 4 functional block:
- Address Unit
- Bus Unit
- Instruction Unit
- Execution Unit
Firstly, the physical address from where the data or instruction is to be fetched is calculated, by the address unit. Once the physical address is calculated then the calculated address is handed over to the bus unit. More specifically we can say, that the calculated address is loaded on the address bus of the bus unit.
This address specifies the memory location from where the data or instruction is to be fetched. The fetching of data through the memory is done through the data bus. For faster execution of instruction, the BU fetches the instructions in advanced from the memory and stores them in the queue.
This is done through the bus control module. As we have discussed that the prefetched instructions are stored in a 6-byte instruction queue. This instruction queue then further sends the instruction to the instruction unit.
The instruction unit on receiving the instructions now starts decoding the instruction. As instructions are stored in prefetched queue thus the decoder continuously decodes the fetched instructions and stores them into decoded instruction queue.
Now after the instructions gets decoded then further these are needed to be executed. So, the instructions from decoded instruction queue are fed to the execution unit. The main component of EU is ALU i.e., arithmetic and logic unit that performs the arithmetic and logic operations over the operand according to the decoded instruction.
Once the execution of the instruction is performed then the result of the operation i.e., the desired data is send to the register bank through the data bus.
As we have already discussed that 80286 is just a modified version of 8086. The register set in 80286 is same as that of 8086 microprocessor.
- It holds 8 general purpose registers of 16 bit each.
- It contains 4 segment register each of 16-bit.
- Also has status and control register and instruction pointer.
Interrupt of 80286 Microprocessor
We know that whenever an interrupt gets generated in a system, then the execution of the current program is stopped and the execution gets transferred to the new program location where the interrupt is generated.
But once the interrupt gets executed then then in order to get back to the original program, its address as well as machine state must be stored in the stack. Basically there exist 3 categories of interrupt in 80286 microprocessor:
- External interrupt (Hardware interrupt)
- INT instruction interrupt (Software interrupt)
- Internally generated interrupt due to some exceptions
External or hardware initiate interrupt are those interrupts that gets generated due to an external input. And are basically of two types:
- Maskable interrupt
- Non-maskable interrupt
Sometimes when multiple programs are allowed to be executed in a system, then this leads to generation of INT instruction, and such an interrupt is known as software interrupt.
Another interrupt in 80286 exist due to some unusual conditions or situations generated in the system that leads to prevention of further execution of the current instruction.
So, this is all about the modes of operation, architecture and interrupts of 80286 microprocessor.
8086 Microprocessor Architecture Pdf
You Might Also Like:
In the changing world of technologies, the devices used are also changing. Let us take a look at the changes between 8085 series of microprocessors and 8086 series of microprocessors.
| Serial No. | 8085 microprocessor | 8086 microprocessor |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The data bus is of 8 bits. | The data bus is of 16 bits. |
| 2 | The address bus is of 16 bits. | The address bus is of 20 bits. |
| 3 | The memory capacity is 64 KB.Also 8085 Can Perform Operation Upto 2^8 ie. 256 numbers. A number greater than this is to taken multiple times in 8 bit data bus. | The memory capacity is 1 MB.Also 8086 Can Perform Operation upto 2^16 ie. 65,536 numbers. |
| 4 | The input/output port addresses are of 8 bits. | The input/output port addresses are of 8 bits. |
| 5 | The operating frequency is 3.2 MHz. | The operating frequency is 5 MHz, 8MHZ,10MHZ. |
| 5 | 8085 MP has Single Mode Of Operation. | 8086 MP has Two Modes Of Operation. 1. Minimum Mode = SingLe CPU PROCESSOR 2. Maximum Mode = Multiple CPU PROCESSOR. |
| 6 | It not have multiplication and division instructions. | It have multiplication and division instructions. |
| 7 | It does not support pipe-lining. | It supports pipe-lining as it has two independent units Execution Unit (EU) and Bus Interface Unit (BIU). |
| 8 | It does not support instruction queue. | It supports instruction queue. |
| 9 | Memory space is not segmented. | Memory space is segmented. |
| 10 | It consists of 5 flags(Sign Flag, Zero Flag, Auxiliary Carry Flag, Parity Flag, Carry Flag). | It consists of 9 flags(Overflow Flag, Direction Flag, Interrupt Flag, Trap Flag, Sign Flag, Zero Flag, Auxiliary Carry Flag, Parity Flag, Carry Flag). |
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important CS Theory concepts for SDE interviews with the CS Theory Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready.
Recommended Posts:
If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using contribute.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to contribute@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Block Diagram Of 8086 Microprocessor
Please Improve this article if you find anything incorrect by clicking on the 'Improve Article' button below.

Difference Between 8086 And 80286 Microprocessor Pdf File